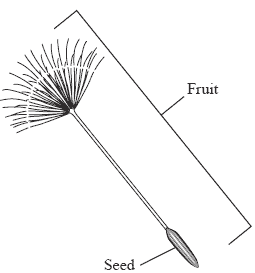
When the fruits of a flowering plant are ripe, the seeds are released. If all the seeds were drop beneath the parent plant, overcrowding would occur. The young plants would have compete with one another and the parent plant for water,light,nutrients and space.
To prevent overcrowding, plants disperse their seeds with the help of wind,water or animals so that the seeds will be scattered far from the parent plants and the other seeds. Some plants split their fruits open with an explosive force to disperse their seeds.
Between the pong pong fruit and the durian fruit, can you tell how their seeds are dispersed by wind, water or animals from their characteristics?
Besides protecting the seeds, fruits also help plants to disperse their seeds.

After pollination, each pollen grain will develop a tiny tube which grows down towards the ovary to meet the egg in the ovule.
The nucleus of the male reproduction cell fuses with the egg. The fusion of a male reproductive cell with an egg to form a fertilised egg is called fertilisation.
After fertilisation, the petals and the parts which help in pollination wither and drop off. The ovary develops into a fruit, while the ovules inside the ovary develop into seeds. These seeds carry the fertilised eggs and will eventually develop into new plants. The fruit carries and protects the seeds until they are released when the fruit is ripe.

For sexual reproduction to take place,the pollen grains from the male part must land on the female part so that the egg can be fertilised.
Pollen is powder-like and each pollen grain is small and light. It can be carried by wind or insects from the anther to stigma of the same or another flower. The transfer of the pollen from the anther to the stigma is called pollination.
Insects, such as bees, butterflies and moths, are important pollinators.
Flowers which are pollinated by insects usually have colourful petals or pleasant scent to attract the insects. The insects are usually rewarded with nectar in the flowers.

Flowering Plants produce flowers for reproduction.The purpose of reproduction is to pass on their generations by dispersing the seeds by wind,water,splitting or maybe by animals or human beings.The female part of a flower consists of the ovary and stigma. The ovary has one or more ovules,each of which female reproductive cell called an egg(ovum).
The male part of a flower has a thin stalk with an anther at its tip. The anther is made up of pollen sacs which contain pollen grains. The male reproductive cells in the pollen grains can fertilise the eggs. A fertilised egg which can develop into a young plant.
In flowering plants,male reproductive cell joins with a female reproductive cell(egg) to produce a fertilised egg which can develop into a new plant. This kind of reproduction,which involves the union of a male and the female reproductive cell,is called sexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants involves the following for processes: pollination, fertilisation, seed dispersal and germination.